How do I bridge network interfaces?
Solution 1:
Since Ubuntu 15.04 you can use the NetworkManager GUI for that:
How to configure a Linux bridge with Network Manager on Ubuntu
The easiest way to create a bridge with Network Manager is via
nm-connection-editor. This GUI tool allows you to configure a bridge in easy-to-follow steps.To start, invoke
nm-connection-editor.$ nm-connection-editorThe editor window will show you a list of currently configured network connections. Click on "Add" button in the top right to create a bridge.
Next, choose "Bridge" as a connection type.
Now it's time to configure a bridge, including its name and bridged connection(s). With no other bridges created, the default bridge interface will be named
bridge0.Recall that the goal of creating a bridge is to share your Ethernet interface via the bridge. So you need to add the Ethernet interface to the bridge. This is achieved by adding a new "bridged connection" in the GUI. Click on "Add" button.
Choose "Ethernet" as a connection type.
In "Device MAC address" field, choose the interface that you want to enslave into the bridge. In this example, assume that this interface is
eth0.
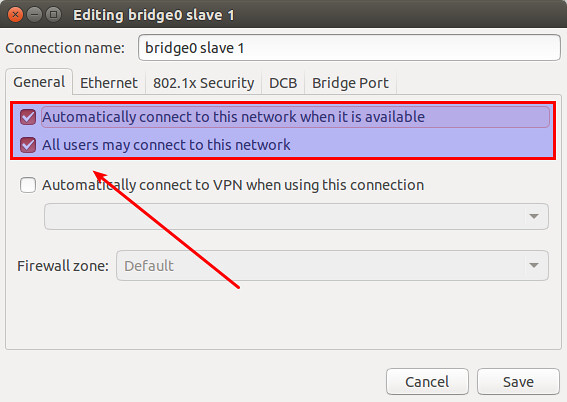
Click on "General" tab, and enable both checkboxes that say "Automatically connect to this network when it is available" and "All users may connect to this network".
Save the change.
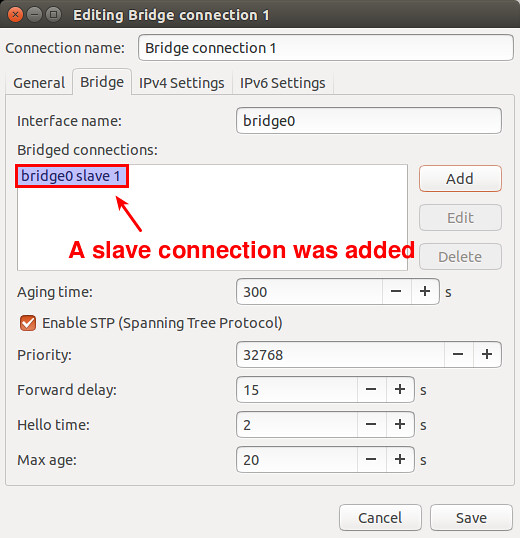
Now you will see a new slave connection created in the bridge.
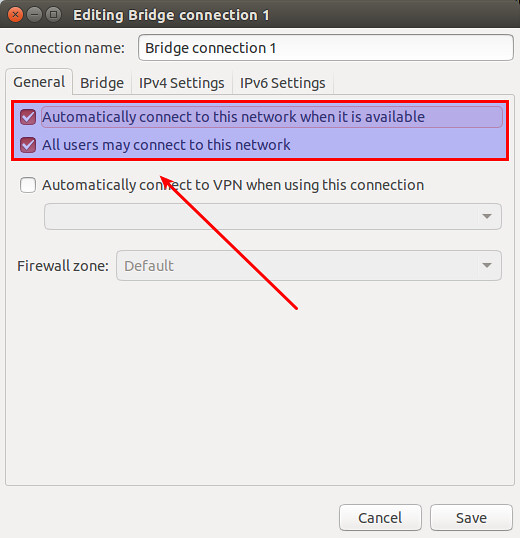
Click on "General" tab of the bridge, and make sure that top-most two checkboxes are enabled.
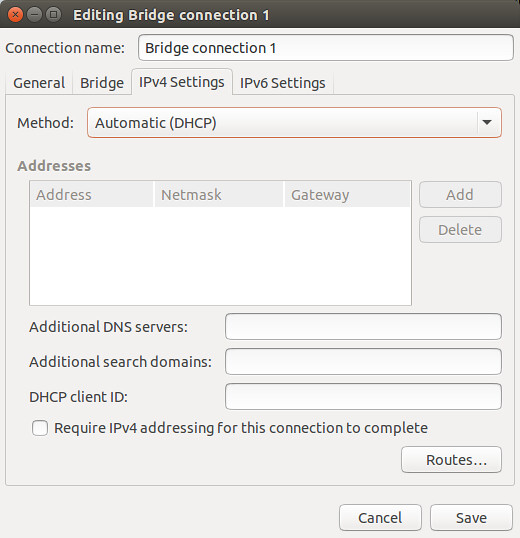
Go to "IPv4 Settings" tab, and configure either DHCP or static IP address for the bridge. Note that you should use the same IPv4 settings as the enslaved Ethernet interface eth0. In this example, we assume that
eth0is configured via DHCP. Thus choose "Automatic (DHCP)" here. Ifeth0is assigned a static IP address, you should assign the same IP address to the bridge.
Finally, save the bridge settings.
Now you will see an additional bridge connection created in "Network Connections" window. You no longer need a previously-configured wired connection for the enslaved interface
eth0. So go ahead and delete the original wired connection.
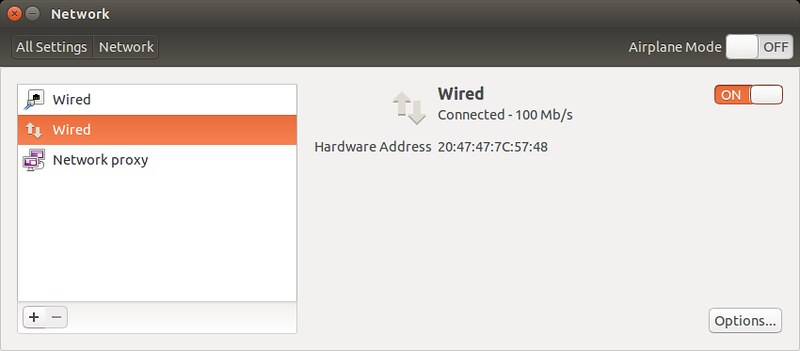
At this point, the bridge connection will automatically be activated. You will momentarily lose a connection, since the IP address assigned to
eth0is taken over by the bridge. Once an IP address is assigned to the bridge, you will be connected back to your Ethernet interface via the bridge. You can confirm that by checking "Network" settings.
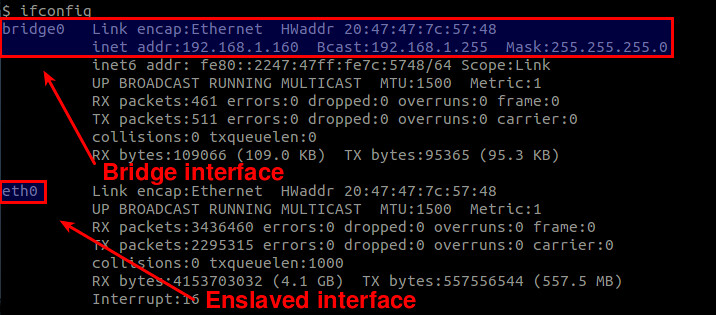
Also, check the list of available interfaces. As mentioned, the bridge interface must have taken over whatever IP address was possessed by your Ethernet interface.
That's it, and now the bridge is ready to use!
(Source)
Other resources:
Network Connection Bridge (Community Wiki)
Bridging Network Interfaces (Community Wiki)
Solution 2:
Yes, that is what you need to do. Sharing an internet connection using Network Manager will setup the sharer as a DHCP server, etc, which is not what you want.
You can read how to do it here: http://manpages.ubuntu.com/manpages/lucid/en/man5/bridge-utils-interfaces.5.html