How to run 'sudo' command in windows [duplicate]
Solution 1:
There is no sudo command in Windows. The nearest equivalent is "run as administrator."
You can do this using the runas command with an administrator trust-level, or by right-clicking the program in the UI and choosing "run as administrator."
Solution 2:
All the answers explain how to elevate your command in a new console host.
What amused me was that none of those tools behave like *nix sudo, allowing to execute the command inside the current console.
So, I wrote: gsudo
Source Code https://github.com/gerardog/gsudo
Installation
Via scoop
- Install scoop if you don't already have it. Then:
scoop install gsudo
Or via Chocolatey
choco install gsudo
Manual instalation:
- Download the latest release, unzip, and add to path, from https://github.com/gerardog/gsudo/releases/
Demo
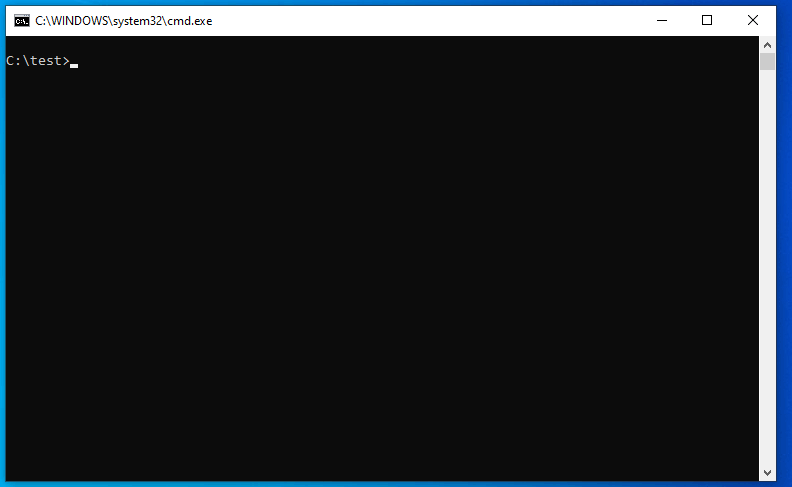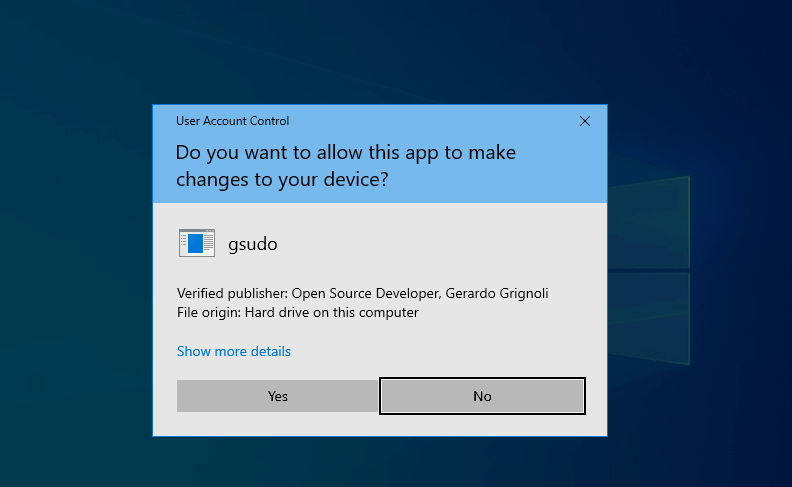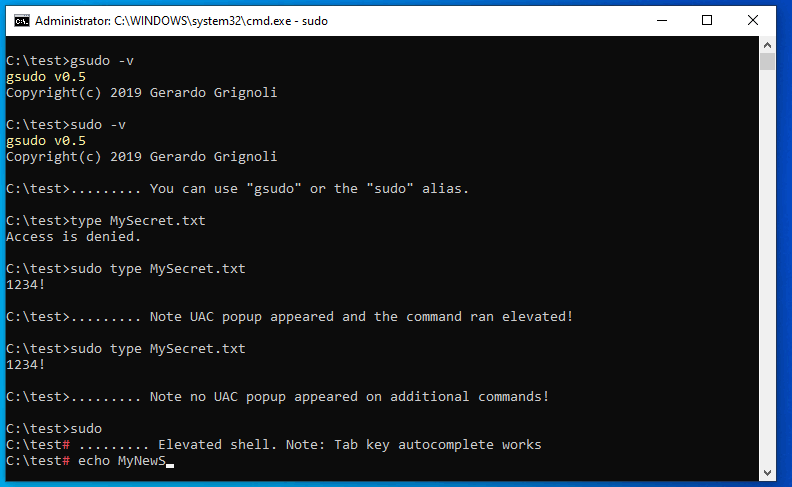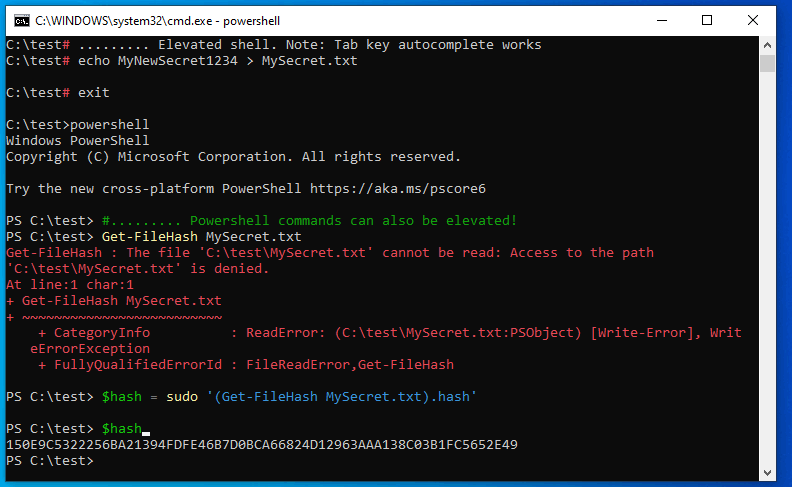
Solution 3:
Open notepad and paste this code:
@echo off
powershell -Command "Start-Process cmd -Verb RunAs -ArgumentList '/c cd /d %CD% && %*'"
@echo on
Then, save the file as sudo.cmd. Copy this file and paste it at C:\Windows\System32 or add the path where sudo.cmd is to your PATH Environment Variable.
When you open command prompt, you can now run something like sudo start ..
If you want the admin command prompt window to stay open when you run the command, change the code in notepad to this:
@echo off
powershell -Command "Start-Process cmd -Verb RunAs -ArgumentList '/k cd /d %CD% && %*'"
@echo on
Explanation:
powershell -Command runs a powershell command.
Start-Process is a powershell command that starts a process, in this case, command prompt.
-Verb RunAs runs the command as admin.
-Argument-List runs the command with arguments.
Our arguments are '/c cd /d %CD% && %*'. %* means all arguments, so if you did sudo foo bar, it would run in command prompt foo bar because the parameters are foo and bar, and %* returns foo bar. cd /d %CD% is a command to go to the current directory. This will ensure that when you open the elevated window, the directory will be the same as the normal window. the && means that if the first command is successful, run the second command.
The /c is a cmd parameter for closing the window after the command is finished, and the /k is a cmd parameter for keeping the window open.
Credit to Adam Plocher for the staying in the current directory code.